8 Critical Disadvantages of EPDM Roofing You Can’t Ignore
Disadvantages of EPDM roofing are more significant than many property owners realize. While EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) rubber roofing is marketed as an affordable, low-maintenance solution for flat and low-slope roofs, it comes with serious drawbacks that can lead to costly problems, requiring expert roofing solutions to address.
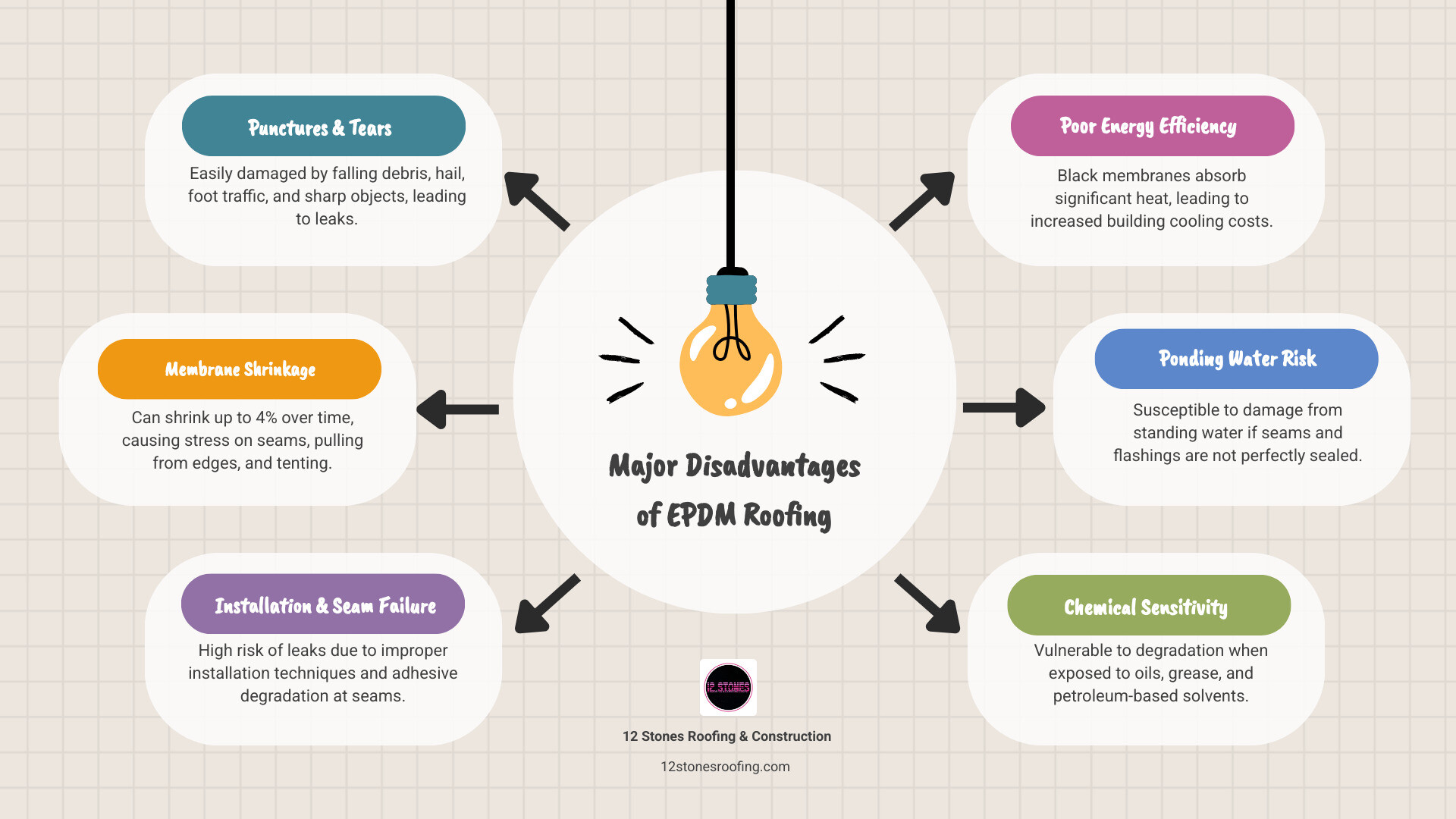
Key disadvantages of EPDM roofing include:
- Susceptibility to punctures and tears from falling branches, hail, foot traffic, and sharp objects
- Membrane shrinkage of up to 4% over time, causing stress on seams and pulling away from edges
- High risk of seam failure due to adhesive degradation, with defects often appearing within the first 3 years
- Poor energy efficiency as black membranes absorb heat, significantly increasing cooling costs
- Installation challenges where improper technique leads to premature leaks and system failure
- Vulnerability to ponding water, which can cause rot, mold, and structural damage if seams aren’t perfectly sealed
- Chemical sensitivity to oils, grease, and petroleum-based solvents
- Limited aesthetic appeal with a dull, flat “inner tube” appearance
EPDM roofing can shrink by up to 4%, causing it to bridge across the substrate like a drum skin rather than fitting snugly. This phenomenon leaves your EPDM roof and building most susceptible to damage. Field seams in EPDM installations can develop defects within the first three years after installation due to application errors or adhesive failure. While EPDM material costs roughly $0.80 per square foot, installation adds $1.50 to $3 per square foot, and the total cost of ownership—including frequent repairs ranging from $50 to $2,000—can quickly exceed initial savings.
For property owners in Pasadena and the greater Houston area, these vulnerabilities are especially concerning given our region’s intense sun, severe storms, and heavy rainfall. The combination of extreme Texas weather and EPDM’s inherent weaknesses creates a perfect storm for issues best addressed by specialized EPDM roofing services far sooner than expected.
I’m Jason Roberts, owner of 12 Stones Roofing & Construction, and over the past decade I’ve witnessed the disadvantages of EPDM roofing through hundreds of emergency repair calls and premature replacement projects. My team’s direct experience with EPDM failures—from punctured membranes after hailstorms to widespread seam adhesive breakdowns—has given us unique insight into why this material often underperforms in the Gulf Coast climate.
Punctures, Tears, and Shrinkage: The Physical Failures of EPDM
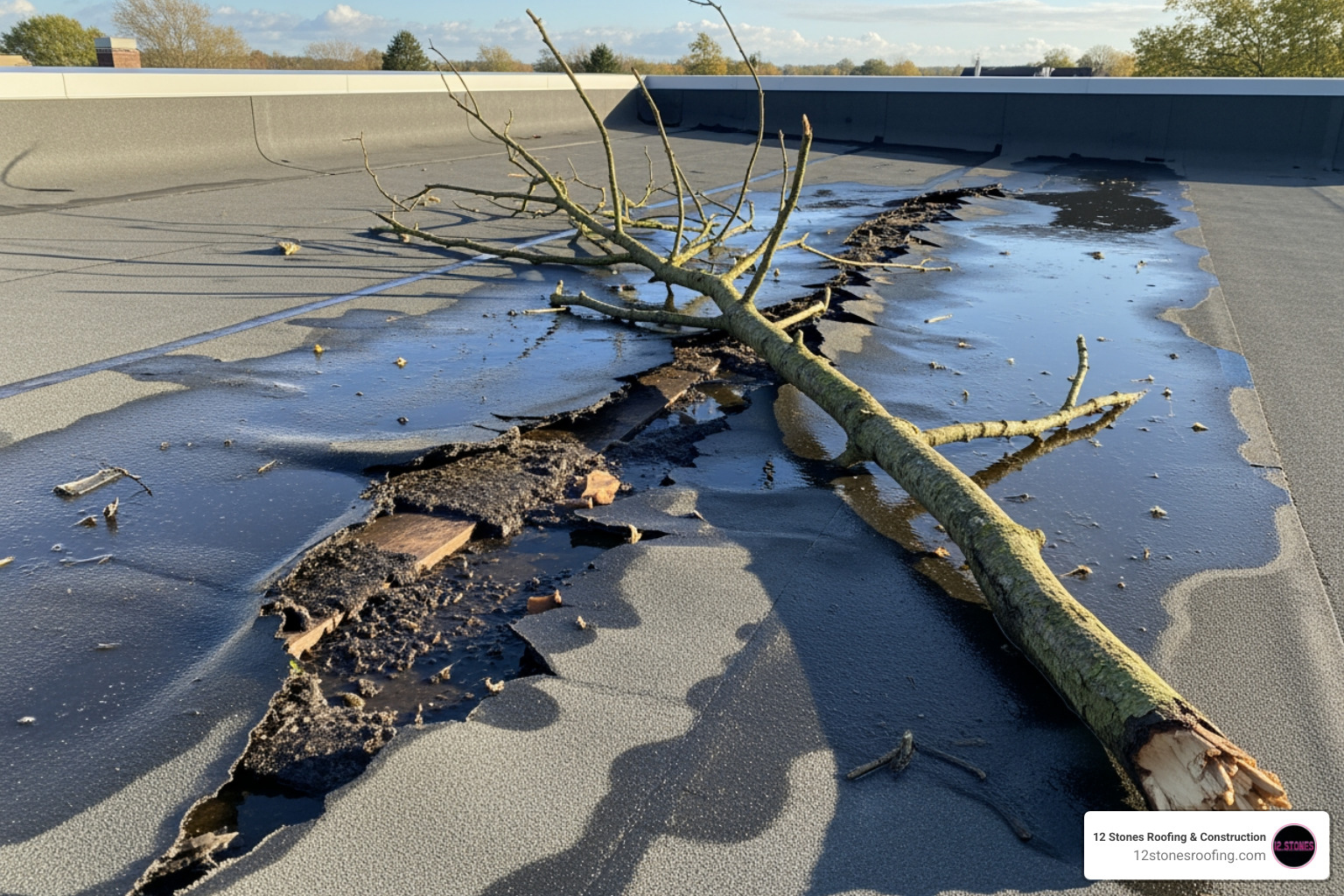

EPDM’s synthetic rubber composition, while flexible, is not immune to physical damage. Its surface is relatively soft, making it one of the most significant disadvantages of EPDM roofing when exposed to common rooftop hazards. These vulnerabilities can compromise the entire roofing system, leading to leaks and extensive water damage.
Susceptibility to Punctures and Tears
One of the most immediate and glaring disadvantages of EPDM roofing is its low puncture resistance. Imagine a thick inner tube stretched across your roof – that’s essentially what an EPDM membrane resembles. While durable in some respects, this rubbery surface is remarkably vulnerable to sharp objects. Falling branches, common during our Texas storms, can easily tear a hole in the membrane. Even a workman wearing the wrong type of boots or dropping a tool can inflict significant damage. We’ve seen instances where hail, particularly the larger hailstones common in our region, has caused widespread punctures and tears.
Once a tear begins in an unreinforced EPDM membrane, it can propagate relatively easily, turning a small incident into a major problem. This susceptibility means that even minor incidents can lead to costly roof repair needs. To mitigate this, some property owners opt for sacrificial layers or protective walkways in areas of heavy foot traffic, but this adds to the overall cost and complexity of the roofing system. Without these precautions, the membrane’s low durability makes it a constant worry, especially in high-traffic or debris-prone environments.
The Problem with Membrane Shrinkage
Another critical disadvantage of EPDM roofing that we frequently encounter is membrane shrinkage. Over time, and particularly due to prolonged UV exposure, the EPDM membrane can shrink by as much as 4%. This isn’t just a minor cosmetic issue; it’s a significant structural problem. As the membrane ages and is exposed to the elements, it loses some of its initial elasticity and begins to pull. This shrinkage causes the EPDM to bridge across the substrate like a drum skin rather than lying flat and securely.
This “drum skin” effect places immense stress on the seams and where the membrane terminates at edges and penetrations. We often see the EPDM pulling away from flashings, creating gaps where water can easily infiltrate. This can also lead to “tenting” at penetrations, such as vents and pipes, as the shrinking membrane pulls taut around them, making these areas highly susceptible to leaks. The compromised flashing, which is meant to seal these critical junctures, can fail prematurely. Proper installation requires giving the membrane enough time to “relax” before securing it, but even then, aging and UV exposure can lead to this problematic shrinkage over the roof’s lifespan. Understanding the materials involved is crucial, and you can learn More about EPDM materials to see how this synthetic rubber behaves.
Installation and Seam Failures: The #1 Cause of Leaks
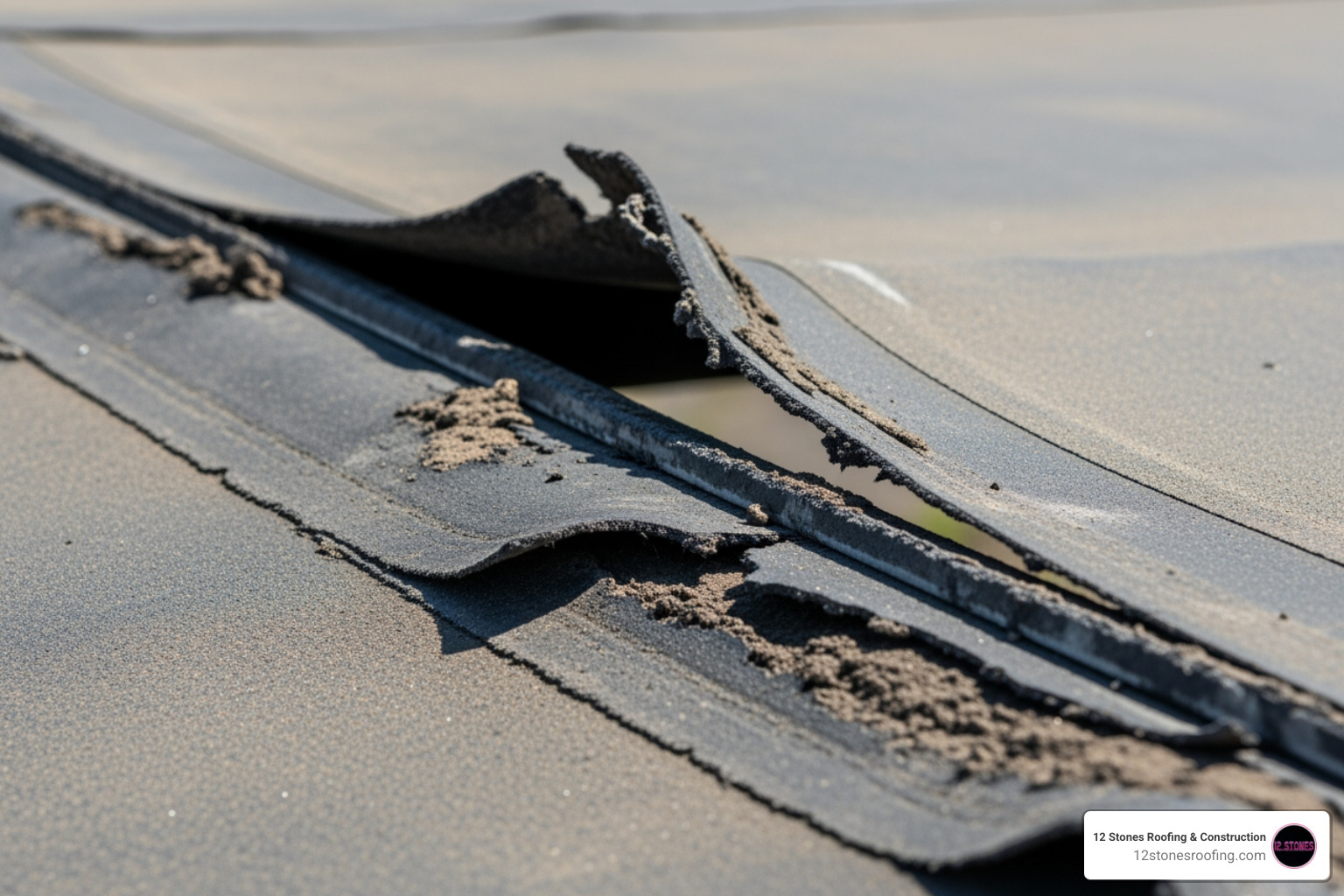

The single greatest point of failure for an EPDM roof is improper installation, particularly at the seams. Unlike systems with heat-welded seams, EPDM relies on adhesives and tapes that require near-perfect application conditions and expert technique to create a lasting, waterproof bond. This reliance on adhesive bonding for watertightness is a fundamental disadvantage of EPDM roofing.
The Critical Role of Installation Quality
The longevity and performance of an EPDM roof are inextricably linked to the quality of its installation. Unfortunately, this is where many disadvantages of EPDM roofing become painfully apparent. We’ve seen countless cases where common installation errors lead to premature roof failure, often within the first three years after the roof was laid.
Inexperienced contractors, who may offer EPDM because it doesn’t require specialized equipment like hot-air welders, can easily make critical mistakes. These errors include improper cleaning of surfaces before adhesive application, applying adhesive too thinly or unevenly, or even installing the membrane in less-than-ideal weather conditions where moisture can compromise the bond. The thickness of the adhesive layer is more critical for a lasting bond than just surface cleanliness. When these details are overlooked, adhesive failure becomes inevitable, leading to leaks and significant water damage. The long-term effects of poor roof installation are devastating, changing what should be a durable roof into a source of constant headaches and expense.
Vulnerable Seams and Protrusions
EPDM’s seams are notorious weak points. Unlike the heat-welded seams of materials like TPO or PVC, EPDM seams are typically glued or taped together. While manufacturers have improved adhesives over the years, these bonds are still susceptible to degradation over time, especially with constant exposure to UV radiation and temperature fluctuations. This makes seam integrity a major disadvantage of EPDM roofing.
Our experience shows that leaks frequently originate from these vulnerable seams. Beyond the seams, roof protrusions—such as vents, pipes, skylights, and HVAC units—are also high-risk areas. Flashing, which seals the membrane around these elements, relies on adhesives that can fail, leading to leaks. Even a small error around a roof protrusion can leave an EPDM roof vulnerable to water ingress. Furthermore, ponding water, a common issue on flat roofs, can put additional stress on these adhesive-dependent seams, accelerating their failure and leading to rot or mold if not properly mitigated. Regular inspections, as detailed in this Technical guide on inspecting EPDM, are essential to catch these issues early.
Heat Absorption and Environmental Drawbacks of EPDM
Beyond physical damage and installation issues, EPDM has inherent performance and environmental disadvantages. Its standard black color can turn a roof into a heat magnet, while its chemical composition raises questions about its environmental footprint and long-term stability.
Poor Energy Efficiency and Heat Absorption
One of the most impactful disadvantages of EPDM roofing, particularly in our hot Texas climate, is its poor energy efficiency. Standard EPDM membranes are black, which means they absorb a significant amount of heat from the sun. This heat absorption directly translates to higher indoor temperatures and, consequently, increased cooling costs for the building owner. In places like Pasadena and Houston, where summers are long and hot, a black EPDM roof essentially acts as a giant heat sink, making it difficult and expensive to keep a property cool.
While white EPDM is available and can help reflect heat, it comes with a significant caveat: it adds approximately 30% more to the material cost per square foot. This additional expense often negates the initial cost-effectiveness that draws many to EPDM in the first place. For commercial roofing projects where energy efficiency is a crucial factor in operational costs, this heat absorption is a major drawback that can lead to a larger carbon footprint and higher utility bills over the roof’s lifespan.
The Aesthetic and Environmental Disadvantages of EPDM Roofing
Aesthetics might not be the top priority for every commercial building, but the dull, flat appearance of EPDM roofing is undeniably one of its disadvantages of EPDM roofing. It often resembles a stretched-out inner tube and can be an eyesore, particularly on low-slope roofs visible from higher vantage points or adjacent buildings. While some commercial property owners may overlook this for perceived functional benefits, it certainly detracts from curb appeal compared to more modern or visually appealing flat roofing options.
From an environmental perspective, EPDM’s origins present concerns. It is produced from oil and natural gas by-products, making it an oil-dependent material. While EPDM can be recycled, its production and disposal processes can still have a negative environmental impact. Furthermore, EPDM has a notable vulnerability to certain chemicals. It can be significantly damaged by exposure to grease, animal fats, oils, and petroleum solvents. This makes it a less suitable choice for certain commercial applications, such as restaurants or industrial facilities, where such substances might come into contact with the roof. In these scenarios, alternative materials like PVC, which are more resistant to these chemicals, are often a better, more durable choice.
The Hidden Costs of EPDM: Why Initial Savings Disappear
While EPDM is often chosen for its low upfront cost, the total cost of ownership can be surprisingly high. Frequent maintenance, the high probability of repairs, and a potentially shorter-than-advertised lifespan can quickly erode any initial savings, making it a less valuable investment over time. This discrepancy between initial cost and long-term value is a significant disadvantage of EPDM roofing.
Ongoing Maintenance and Repair Costs
The perceived low maintenance of EPDM roofing is often misleading. To prevent the numerous issues we’ve discussed, regular maintenance is absolutely required. This means conducting inspections every 3-4 months, diligently removing dirt and debris, and carefully checking seams and flashings for any signs of degradation or failure. Neglecting these tasks can lead to accelerated deterioration and significant problems.
When issues do arise, the costs can add up quickly. While a small EPDM repair might cost $50-$100, more extensive repairs can range from $1,000-$2,000. These aren’t isolated incidents; EPDM roofs often begin to leak and fail prematurely, long before their projected service life. If you find yourself undertaking substantial repairs on an EPDM roof repeatedly, it may be wiser to consider a full roof replacement with a more reliable material. The initial savings on EPDM can quickly be overshadowed by these ongoing maintenance and repair expenses, making its overall value proposition questionable.
To illustrate, let’s compare EPDM with TPO, a common alternative, across key performance indicators:
| Feature | EPDM Roofing | TPO Roofing |
|---|---|---|
| Puncture Resistance | Low (easily damaged by sharp objects, foot traffic, hail) | Higher (more resistant to impacts and abrasion) |
| Seam Strength | Glued/Taped (prone to adhesive failure, leaks) | Heat-welded (creates a strong, watertight bond) |
| Energy Efficiency | Poor (black membrane absorbs heat, increases cooling costs) | Good (typically light-colored, reflects heat, reduces cooling costs) |
| Average Lifespan | 12-25 years (often fails prematurely due to installation/maintenance issues) | 20-30+ years (durable, fewer seam failures) |
Frequently Asked Questions about EPDM Roofing
Is EPDM a bad roofing material?
EPDM is not inherently “bad,” but it has significant disadvantages that make it less suitable for certain applications and climates. Its high susceptibility to installation error, punctures, and heat absorption means that other materials like TPO or PVC often provide better long-term value and performance. While it might be a budget-friendly option upfront, the potential for premature failure, expensive repairs, and increased energy bills can quickly diminish its appeal. For many property owners, especially in demanding climates like Pasadena, TX, the risks associated with EPDM outweigh its benefits.
How long does an EPDM roof really last?
While manufacturers may warranty the material for 20 years or more, the actual service life of an EPDM roof system is often shorter. Failures related to seams, flashing, and punctures can occur in as little as 3-7 years if the roof was poorly installed or is not regularly maintained. We’ve seen EPDM roofs in the Houston area begin to show significant signs of wear and tear, including widespread leaks, well before their expected lifespan due to our intense UV exposure and severe weather events. The “lifespan” often touted is under ideal conditions, which rarely reflect real-world scenarios.
Can you walk on an EPDM roof?
Walking on an EPDM roof is possible but should be done with extreme caution. The membrane is easily punctured by sharp objects underfoot, such as screws, rocks, or even abrasive-soled boots. We recommend minimizing foot traffic as much as possible. For roofs requiring regular access for maintenance of HVAC units or other rooftop equipment, installing designated protective walkways or sacrificial layers is essential to prevent damage. Without these precautions, even routine inspections can inadvertently lead to costly punctures. For more details on EPDM care, you can consult the EPDM Roofing Association FAQs.
Is EPDM Roofing Right for Your Property?
While EPDM roofing presents a low initial cost, its numerous disadvantages—from a high risk of punctures and seam failure to poor energy efficiency and shrinkage—demand careful consideration. For property owners in Pasadena, TX, where intense sun and storm activity are common, these drawbacks can lead to frequent, costly problems. The success of an EPDM roof is almost entirely dependent on a flawless installation, a risk that many property owners may not want to take.
Before making a decision, have your property assessed by professionals who understand the local climate and the full range of available flat roofing solutions. The experts at 12 Stones Roofing & Construction can provide an honest evaluation and help you determine if EPDM or a more durable alternative is the right choice for your building. To protect your investment, contact us today for a comprehensive consultation at (713) 358-4838 or explore our EPDM roofing services.




